Anyone who has seen the 2014 movie Maleficent will know that iron burns fairies and iron chains can hold a dragon captive. Iron frames were once popular for children’s bedsteads, because it was said that fairies could not approach to snatch or swap the infants who slept upon them. Iron bands around the coffin of a witch or a vampire were believed to prevent them from escaping their tombs. Many of the classical texts on Qabalistic ritual warn the magus to keep iron out of their ritual circle, because it ‘earths’ the Magickal powers they attempt to invoke.
Yet iron has also been the saviour of many a church bell ringer, by ‘magically’ attracting lightning and diverting its path down to the earth outside the church, rather than down the bell pull and to the puller. There is earlier evidence of tall buildings using iron as lightning conductors, though use by the Christian Church was not recorded until the 1750s when they were ‘invented’ by Prokop Diviš, a Bohemian priest in Přímětice. This was around the same time as Benjamin Franklin’s more famous experiments with making lightning rods.
The use of lightning rods caused a furor of conflicting arguments from different factions of the Church. Some priests thought that they demonstrated the Church’s ability to control the elements in the name of God. Others argued that they demonstrated a lack of faith in the power of prayer as a form of protection. Some thought the Church was actually endorsing, and dabbling in, what may be a form of witchcraft! Some believed that their use attracted God’s wrath, causing churches to be struck by lightning much more regularly. Others thought lightning strikes occurred because they frustrated the Devil and his followers, making them lash out angrily, though ineffectually. It was claimed that lightning rods also caused earthquakes. However, it seems that bell ringers all said, ‘Thank God!’
By the use of iron, the early church was seen to have tamed and controlled the power of pagan gods, typified by the Viking Thor, or the bolt-throwing Greek god Zeus. Iron became symbolic of the power of the Christian church over older, ‘heathen’ belief systems, and the apparent chaos of the natural world. If iron could tame great old gods such as Thor and Zeus, then certainly it could defuse the pagan powers of witches and pesky demons.
Many properties of iron, as we now understand in scientific terms, must have seemed magical when first observed. An iron needle floating in a bowl of water could tell you which way to steer your ship at sea, even when the stars were obscured by cloud. An electric spark, thought by some to be analogous with life energy, could disappear into an iron filament and come out at the other end, seemingly unchanged. Of course, even today, iron still seems magical in many respects. It is the most plentiful metal in the universe. All iron was initially forged in the hearts of stars, and only gifted to the cosmos when they exploded in supernovae. This stardust is in each of us; it is what makes our blood red.
The earliest iron artefacts were made millennia before the Iron Age, from meteoric iron that had fallen from the sky. This was when the sky was still the realm of the gods. Therefore, iron was a gift from the gods, and must be imbued with godly powers. Accordingly, these first artefacts were fit for our gods on earth. For example, the pharaoh Tutankhamun.
Some of the earliest known fairy tales concern iron and the art of the blacksmith. I have already touched upon the origins of fairy tales in a previous article here on #FolkloreThursday, along with their connection to iron and why horseshoes are said to be lucky and ward off evil if hung over your doorway.
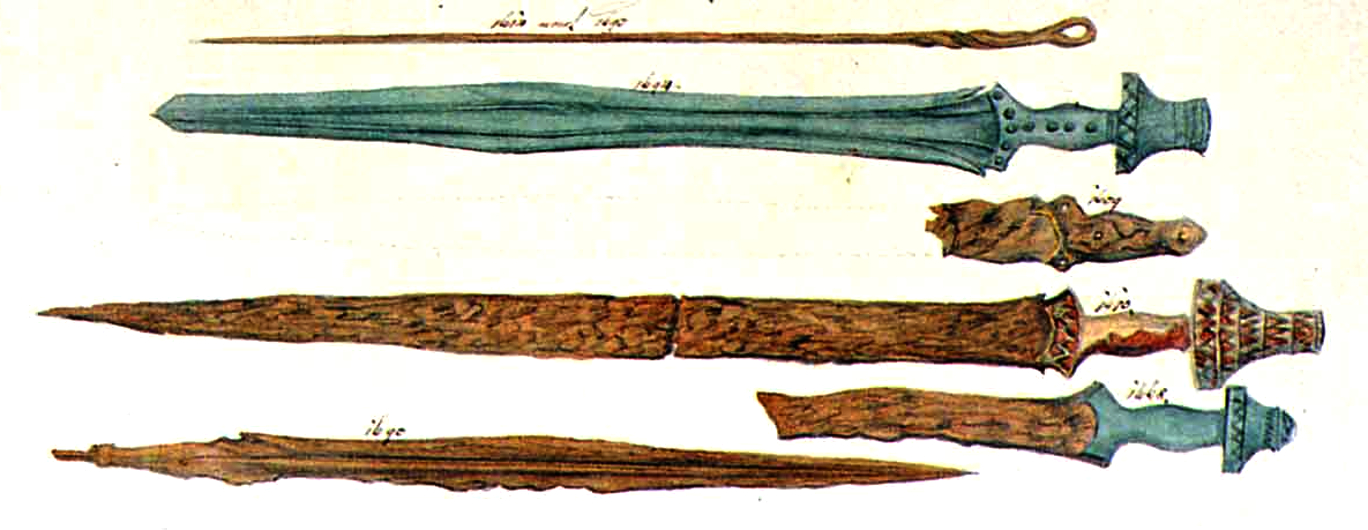
The lore that surrounds iron has changed from beneficent to maleficent and back again as many times as historical conflicts and conquests have changed the ideology of the dominant culture. It seems that the smelting and use of iron developed independently in several locations around the world. The Iron Age is generally understood as the period during which the technology to make iron items — particularly weapons — spread from the Hallstatt culture in western and eastern Europe during the 8th century BCE. It radiated out through Celtic Europe, eventually reaching Britain, and then expanded into the La Tène culture during the 4th century BCE.
Clearly, the peoples of this extended period did not one night go to sleep in the Bronze Age and awaken the next morning in the Iron Age. There were considerable overlaps as the technology of iron developed and travelled throughout the European continent by way of trade. This also appears to coincide with a violent period of history, with hill forts springing up all across the British Isles, particularly in the southern regions.
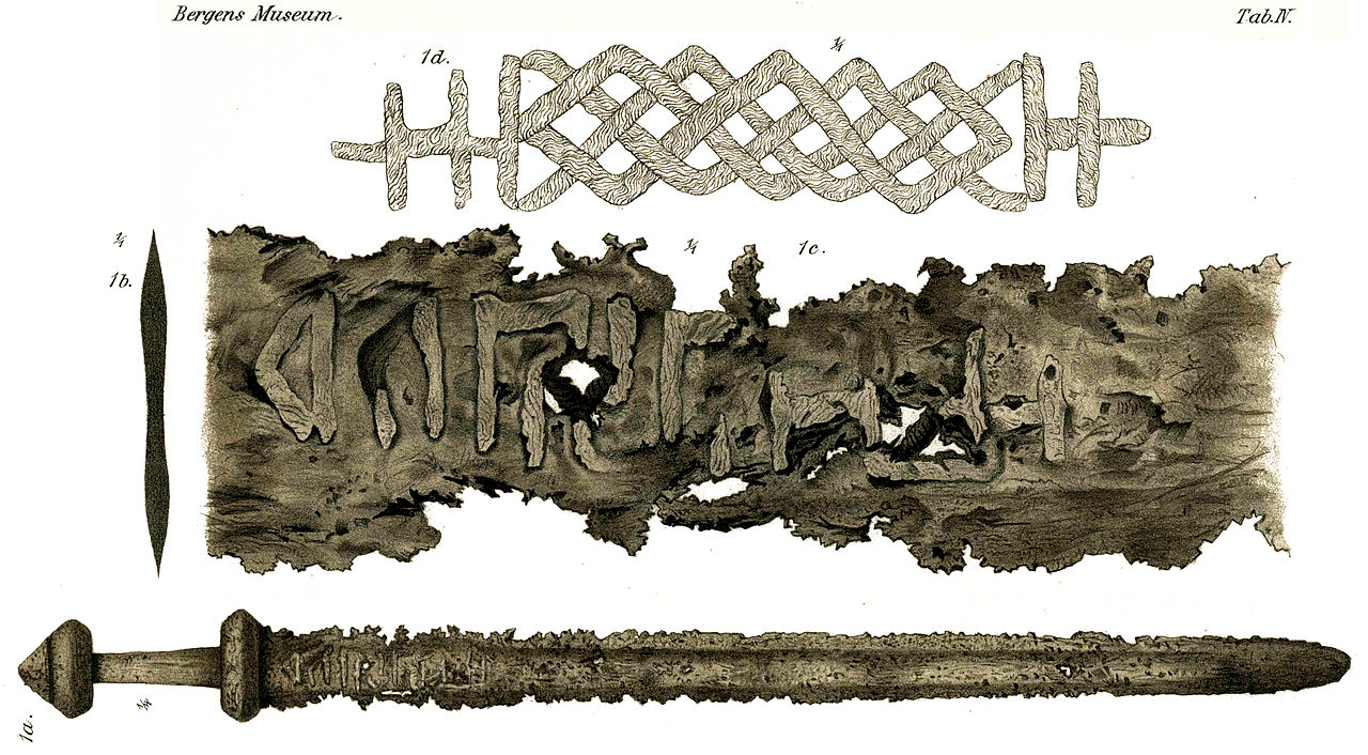
It is also interesting to note that bronze ‘carps-tongue swords’ in the Hallstatt style were popular trade items, appearing in Britain during the early period of the Iron Age of central Europe. These were beautiful and stylistically sophisticated swords and yet, technologically, they were already outmoded. This is just like international arms dealing today! Sell potential enemies inferior or out-dated weapons, and keep the superior tech for your own armies. So, the Britons were trading peacefully, and at the same time building defensive forts and preparing for battle. Imagine their surprise when the clashes came with the peoples who had made the swords they were using. It must have been baffling when enemy blades just seemed to cut right through theirs, and also their shields.
The Britons had a reputation for being small in stature yet fierce warriors, and possibly adept at magic. They seemed to be able to appear and vanish at will from among the trees of the forests and among the hills. According to some early Roman accounts, the Britons would spike their hair with white lime and cover their bodies in swirling patterns of blue woad for battle, possibly to enable them to vanish into the pattern of clouds in the sky or reflected on the surface of lakes. This resulted in a belief that they could appear out of thin air and make their getaways via ‘portals’ in lakes and rivers. Some have suggested that this is where the myth of the fairy folk began. These ‘fairy folk’ who used ‘magical’ tactics were armed with bronze, which was no match for the iron blades of the invaders. Therefore, iron became known as the enemy of the ‘fairy folk.’
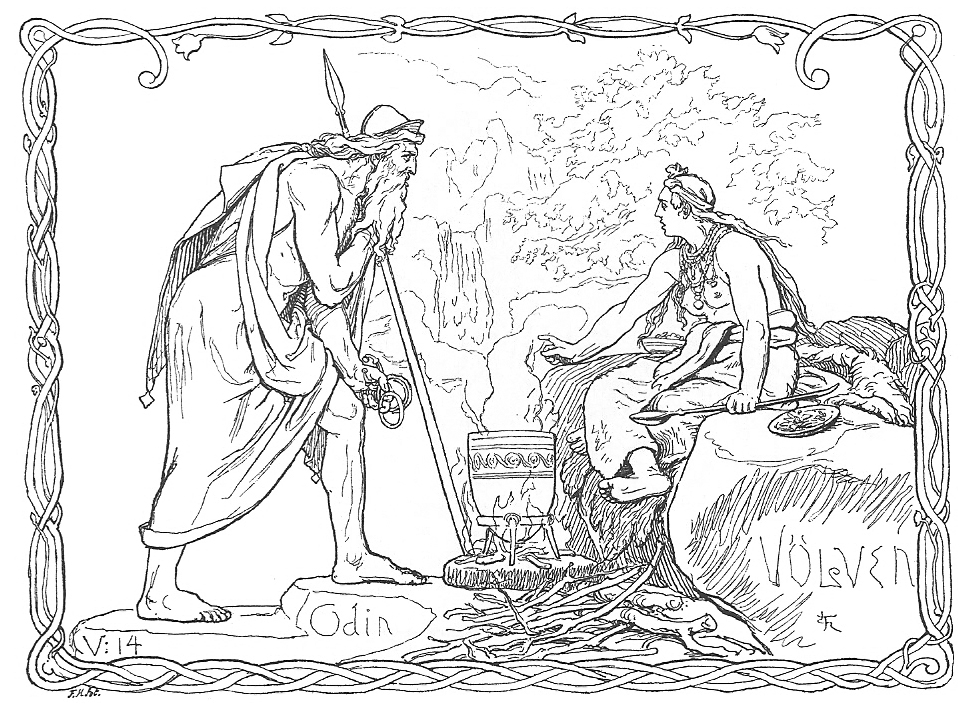

In Wicca, wands are usually made from hazel or rowan – grown things of natural origin, reinforcing the connection with the seasons and cycles of nature, with which we work in harmony. However, the wands of the Norse Vǫlva shamans were iron, implying that for them magic was a human thing involving forging and manipulating natural resources and elemental forces according to our will.
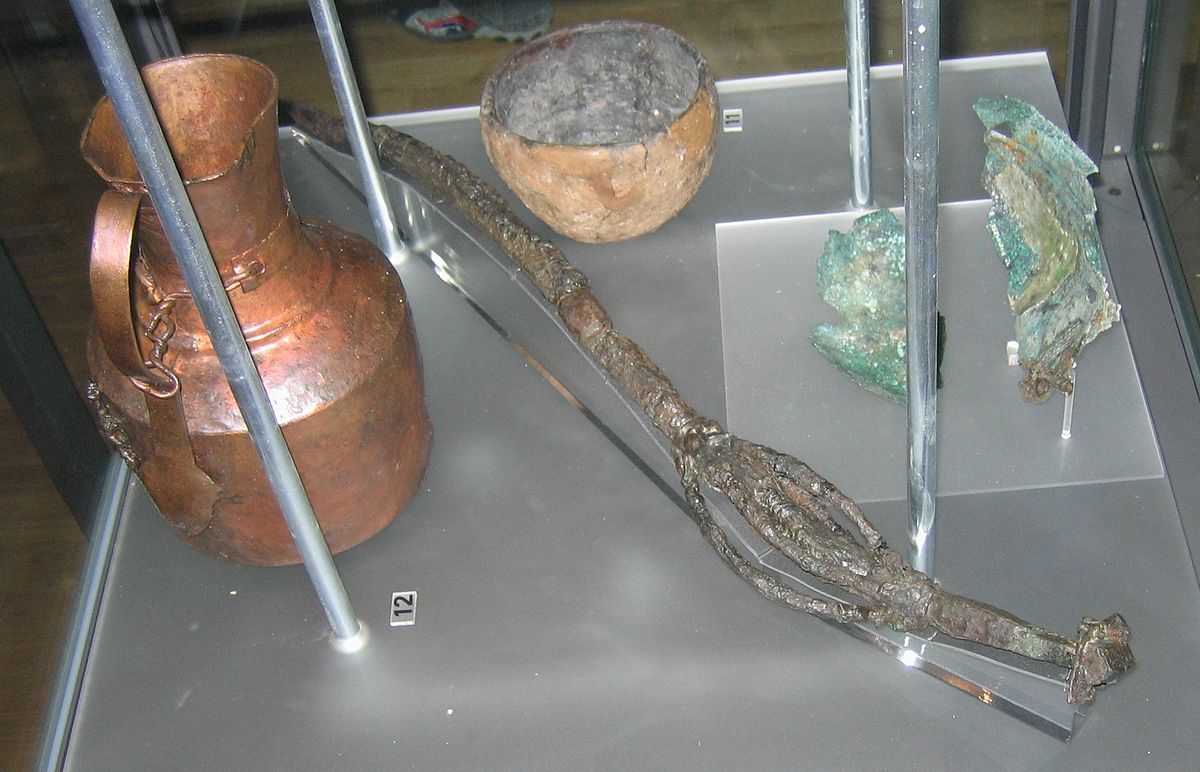

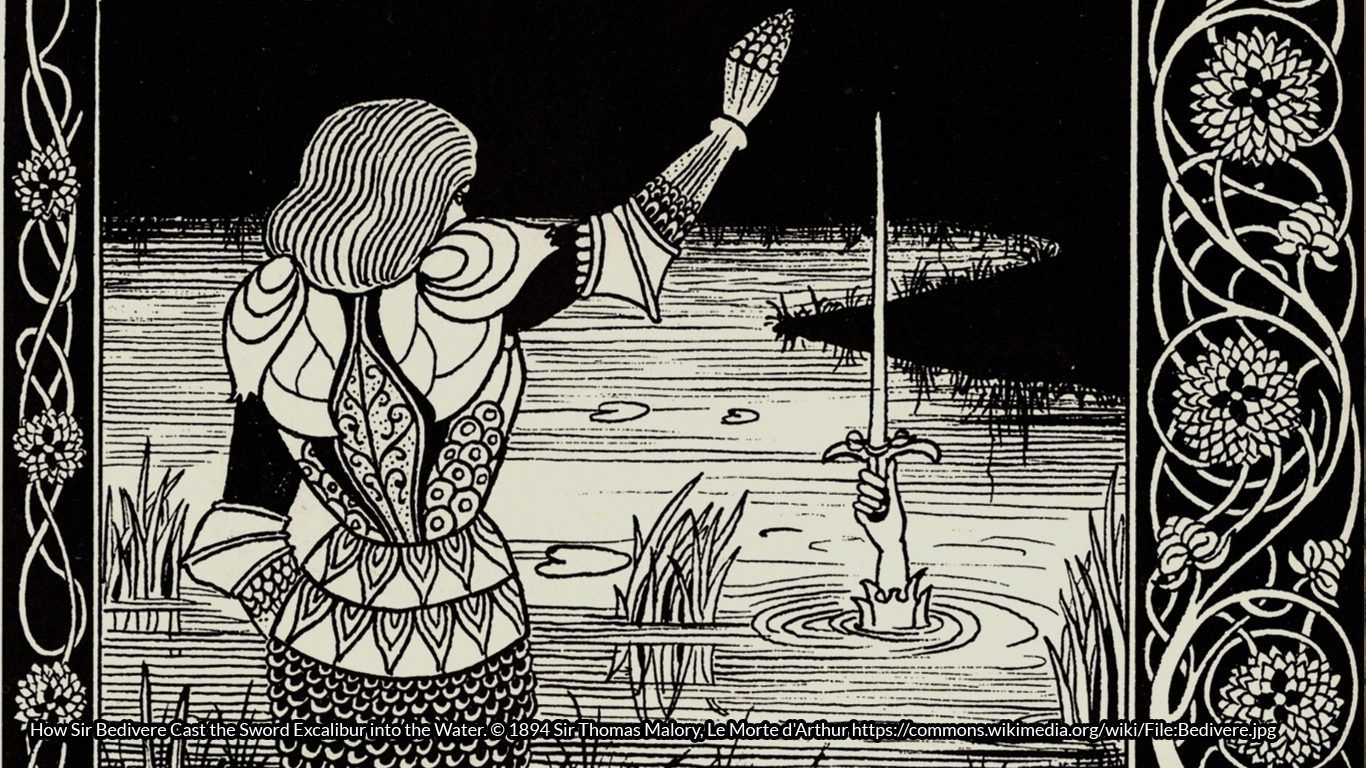
Siberian shamans traditionally make magical artefacts from iron, perhaps owing to their ancestral heritage. The name ‘Russia’ is derived from the Russ, a pre-Viking Norse clan who were founders of the settlement that became modern Moscow. This brings us nicely around to a famous iron sword, perhaps the most famous sword of all time: Excalibur.
Viking swords were prized by non-Vikings for a number of reasons, including their strength, balance, quality, and reputation. There were only a few ways that a non-Viking may come by a Viking sword. Possession of one indicated that you were very wealthy and had gained the respect of a wealthy Viking, or had defeated a Viking warrior in battle – both impressive achievements. So, could Excalibur have been a Norse-forged iron sword? We know that such weapons were often cast in moulds made of stone, so the ‘sword-in-the-stone’ bit would certainly fit. True, the Viking era came several centuries after the Iron Age, but myths and legends are often stories amalgamated from several earlier sources. Also, if remembered from the pre-Viking crossover period from Bronze to Iron Age, a similarly well-balanced, expertly forged iron sword would seem magical due to its ability to cut through bronze blades (and even through weapons made from inferior quality iron).

If magic is an energy, a physical force, then perhaps iron makes more sense as wand material. We know that iron can attract and conduct electricity, focus and release it, store it as magnetic energy, or disperse it by returning it to the earth. Iron can change form. It can be made molten, fluid, and malleable, and then set into unbending forms of our design. Be it blade or wand, the magic of this metal could enable one not only to repel fairies, but to rule with ‘a rod of iron,’ or indeed, ‘the sword of kings.’
References & further reading
Gareth Williams and Peter Pentz, 2014, Vikings: Life and Legend, British Museum Press, ISBN 978-0714123370
Barry Rafferty and Clint Twist, 2001, Atlas of the Celts, Philip’s, ISBN 978-0540078806
Geoffrey Barraclough, 2000, The Times Atlas of World History – A New Edition, Ted Smart / Times Books, ISBN 978-0007619009
Richard Cavendish, 1989, The Magical Arts, Arkana, ISBN 978-0140191523
Magnus Magnusson, 1976, Viking: Hammer of the North, Harpercollins, ISBN: 9780856133015
Richard Cavendish, 1969, The Black Arts, Pan Macmillan, ISBN 978-0330022231
Maria Antonina Czaplicka, 1914, Aboriginal Siberia: A Study in Social Anthropology, Oxford Clarendon Press
Jim Al-Khalili, 2011, Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity, British Broadcasting Corporation and Open University, UK Television











